Katihar District
As per Purnea gazetteer (1799) Governor Nawab Shaif Khan had preferred this place as a safe place for his treasure and called the place as Shaifganj (Sharifganj). Historian Francis Buchanan has also used name Shaifganj for the Katihar. The present district Katihar came into existence in the year 1860 and named after a small village called Dighi-Katihar where a fierce battle was fought between army of the then nawab of Purnea and army of the then nawab of Murshidabad. Katihar was declared Subdivision of Purnea district vide notification of state government dated 24th April 1954 and word Shaifganj was also mentioned in bracket after Katihar.
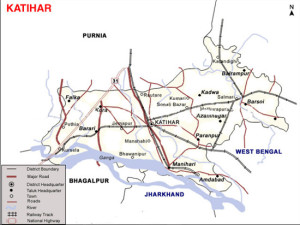
Katihar was carved out from Purnea as a separate district on 2nd October, 1973. This district has three Subdivisions – Katihar, Barsoi and Manihari and sixteen community development blocks.
How To Reach
By Air (Airport) :-
The nearest commercial airport is Bagdogra (160 km) near Siliguri (West Bengal).
By Rail :-
Katihar lies in between Barauni-Katihar section of Barauni – Guwahati line in the Katihar Division under the Northeast Frontier Railway . The Katihar Junction railway station is connected to most of the major cities in India by the railway network. Katihar is famous for Railway Junction of seven Railway lines/routes.
East India Railway Company opened the Manihari-Katihar-Kasba section in 1888 and the North Bengal Railway opened the Katihar-Raiganj section the same year. EIR opened the Barsoi-Kishanganj section in 1889. All these lines were 1,000 mm(3 ft 3 3⁄8 in) wide metre gauge lines. Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, operating 2 ft (610 mm) narrow gauge lines, extended their operations from Siliguri to Kishanganj in 1915.
Katihar – Siliguri line which serves the city with numerous number of trains to Guwahati, Kolkata, Delhi and with many other cities.
Siliguri was connected to Kolkata via the eastern part of Bengal since 1878 (for details see Howrah-New Jalpaiguri Line. However, with the partition of India in 1947, railway services in the region were completely disrupted. In 1949, the narrow gauge Siliguri-Kishanganj section was upgraded to metre gauge. Thus there was a direct metre gauge connection from Manihari to Siliguri via Katihar.the importance of katihar station grew because of the jute mill in the region.
In the early 1960s, Indian Railways took the initiative to extend 1,676 mm (5 ft 6 in) wide broad gauge rail link from Kolkata.The 2,240 m (7,350 ft) long Farakka Barrage carries a rail-cum-road bridge across the Ganges. The rail bridge was opened in 1971 thereby linking the Barharwa-Azimganj-Katwa loop to Malda, New Jalpaiguri and other railway stations in North Bengal.
Gauge conversion work (from metre gauge to broad gauge) in the Barauni–Katihar section was taken up in 1978-79 and completed in 1982.
The major facilities available are Waiting rooms, retiring room, computerized reservation facility, Reservation Counter, Vehicle parking etc. The vehicles are allowed to enter the station premises. There are refreshment rooms vegetarian and non-vegetarian, tea stall, book stall, post and telegraphic office and Government Railway police (G.R.P) office.Automatic ticket vending machines have been installed to reduce the queue for train tickets on the station.
By Road :-
Well connected to other city through National Highway -31,31(EWC), 81 SH-62,65,77 Other road-Katihar Manihari Rd,Korha Falka Rd,Korha Semapur Rd,Raghunathpur Balarampur Rd,Karagola Phulwaria Rd,Katihar Sonaili via Chandarma chowk,Dumar Pothia Rd
Katihar is 341 km from Patna.
Popular tourist destinations
KATIHAR BLOCK
Sarvajanik Durga Mandir (Katihar):-
Jama Masjid Anjum Eslamiya(Katihar):-
Ramakrishna Mission Ashrama(Katihar):- With a small and humble beginning of relief to plague and malaria patients in Katihar-Purnea-Araria in 1925, the Ramakrishna Mission started the regular seva in a small shrine. In meantime they established Ramakrishna Mission Ashrama in this small shirine in year 1926. The devotees then approached the Ramakrishna Math, Belur Math authorities for the affiliation of this centre. The then Most Revered President Maharaj, Swami Shivanandaji, a direct disciple of Shri Ramakrishna, opined, “Katihar is a halting station from Belur Math to Assam. Katihar Ashrama was affiliated to Ramakrishna Math and Mission, Belur Math as a branch centre in 1931.
Gurudwara(Karahgola):- The gurudwara established by Guru Teg Bahadur.
Temple of Goddess Kamakhya(Bhawanipur):- It is located 7 KM towards East from District head quarters Katihar. 292 KM from State capital Patna
MANIHARI BLOCK
Manihari :- The village is situated about 20 km south of Katihar on northern bank of the River Ganga. There is a mythological story that during the Mahabharata period, Lord Krishna had come to this place and had lost a Mani (a valuable jewel ). Thus it came to be known as Maniharan which was changed into Manihari. Located on northern bank of the River Ganga, Manihari gives a picturesque view of both the River Ganga and Rajmahal Hill on the opposite Bank.
Goga Bil Pakshi Vihar:– It is about 26 km south – east of Katihar and east of Katihar-Manihari Rd. Patna is about 300 km away. The nearest railway station is Manihari and Katihar junction is at 25 km. The government of Bihar has declared Goga Bil Pakshi Vihar as a Closed Area. It is 217.99 acres in area. Goga-Bil is an oxbow lake formed by River Kankar. It is a feeding and molting area of more than 300 species & sub-species of birds during monsoon and winter, which migrate from Caspian Sea and Siberian region.
As per the special treaty on the 8th October 1984 between India and erstwhile USSR for the protection of these migratory birds and their foraging ground.
Baghar beel:- Baghar beel is about 28 km southeast of Katihar.The flood waters from Goga Bil during monsoon form wetlands, namely Baghar beel. This wetlands are inundated by overflow from the Gogabil and local monsoon run-off.. Its waterspread becomes about 25 ha in summer from about 400 ha in the monsoon. Baghar beel is oxbow lakes marking the historical course of Gogabil river. As the chaurs dry out, the exposed mud is covered with grasses and creepers. The great part of the exposed lake bed is subsequently brought under cultivation. Water from these wetlands is used for irrigation and domestic supply. It is a feeding and molting area of more species.
Baldia Chaur:- The flood waters from Goga Bil during monsoon form wetlands, namely Baldia chaur.This wetlands are inundated by overflow from the Gogabil and local monsoon run-off Baldia chaur is shallow and is seasonal only. This chaurs is oxbow lakes marking the historical course of Gogabil. As the chaurs dry out, the exposed mud is covered with grasses and creepers. The great part of the exposed lake bed is subsequently brought under cultivation. Water from these wetlands is used for irrigation and domestic supply. It is a feeding and molting area of more species.
Kanchira Wetland (250 23.112” N and 870 37.597” E):- It is situated near Manihari chowk. It spread in an area of about 22 Acre is formed as the result of excavating the ground soil for brickindustry. The site is very closeto the area of Goga Bil, Baghar Beel and Baldia Chaur. The birds found in Kanchira wetland are: Wooly-necked Stork Ciconia episcopus, Bar¬headed Goose Anser Indicus, Red-crested Pochard Netta rufina, Little Cormorant Phalacrocorax niger, Great Cormorant Phalacrocorax carbo, Little Egret Egretta garzetta, Great Egret Casmerodius albus/ Ardea alba Intermediate Egret, Egretta intermedia / Mesophoyx intermedia Indian Pond Heron, Ardeola grayii Grey Heron, Ardea cinerea Purple, Heron Ardea purpurea , Black¬headed Ibis Threskiornis aethiopica / Threskiornis melanocephalus, Black Ibis Pseudibis papillosa Asian Openbill Anastomus oscitans, Lesser Adjutant Leptoptilos javanicus, Asian Pied Starling Sturnus contra Common Myna Acridotheres tristis Brahminy Starling Sturnus pagodarum Citrine Wagtail Motacilla citreola Coppersmith Barbet Megalaima haemacephala. A population of domestic ducks is also seen.The area is surrounded by the agricultural fields and human settlements.
Maharshi Mehi asharam (Manihari):– As directed by his teacher, Mehi spent many years in intense meditation in an ashram located in Manihari near bank of holy river ganga. Now the ashram is known as mahrishi mehi Mandir.The ashram is very popular in that koshi region among local as ‘saadhna asthali ‘ of mystic maharis.
Sri Satmant Satsang Mandir(Manihari):-
Pir Majar(Manihari):-
Gungunia Masjid (Manihari):-
Shiva-linga (Raja Virat):- A place to the east of Manihari at a distance 8 km is connected to the story of Raja Birat of Mahabharata period that had kept a herd of cows at this place and had constructed a Bathan. There is one black stone shiva-linga about five feet in length and three feet in width lying in an open field which is said to be of Raja Birat’s time.
Nawabganj :- It is situated 3 km north of Manihari, noted as the former seat of Nawab Shaukat Jang, Governor of Purnia in the Mughal period. Ruins of palace exist here.
Muswar:- Where Pandavas used to keep their bows and arow-Armery
Baldia-bari :- It is situated about 27 km south -east of Katihar and about 2.5 km from Manihari near the bank of Ganga. It is noted as the site of battle fought between Nawab Siraj-ud-daula of Murshid and Nawab Shaukat Jang, Governor of Purnia in 1756.
BARSOI BLOCK
Belwa :- It is situated about 8 km south of the Barsoi Block Headquarter . It has remains of ancient building and some stone images of Lord Shiva and Goddess Saraswati. A fair is held on the occasion of Basant Panchami every year
Digambar Jain Mandir( Barsoi):-
KADWA BLOCK
Kadva :-
KURSELA BLOCK
Kursela :- It is situated 50 km west – south of Katihar and about 45 km south – west of Purnia on NH 31. A distorted name of Kuru-Shila. Kuru-Shila means hilly part of the region which once belonged to the king Kuru, the descendents of whom were called Kaurawa and according to Mahabharata waged a war with Pandavas, their cousins. It is seat of the Kestate , having a private landing ground.
Bateshwar hills :- It is located 6 km south of the town of Kursela. There is an ancient temple to Mahadeva (Shiva and Vishnu) on the hills. Some associate the once famous Vikramshila University with this site.
KORHA BLOCK
Ukahi :- It is lies near Khorha. It is said that Goddess durga discovered during excavation here. According to legend, one Sone Lal Jha dreamt that he had received divine instruction to excavate a particular place . The image was found at that very spot and later established in a temple.
Durga Mandir( Fulwaria, Khorha):-
AZAMNAGAR BLOCK
Gorakhnath Siva Mandir(Ajamnagar):-
FALKA BLOCK
Purani Jama Masjid(Falka):-
SAMELI BLOCK
Chhohar:- It is situated in Sameli block. As per exploration done by KP Jayaswal Research Institute marked Period of site as Early medieval .
Taj Dehori:- Earlier, Katihar district was dominated by the Choudhary family, who were the biggest landlords of Kosi zone. The founder of Choudhary family was Khan Bahadur Choudhary Mohammad Baksh and he had an authority over 126 small landlords of Kosi zone. He died in 1943. The family holds lands of about 15,000 acres (6,100 ha) in Katihar district, and 8,500 acres in Purnia. Now his successors still live there in a haweli known as Taj Dehori.
AMDABAD BLOCK
BALRAMPUR BLOCK
BARARI BLOCK
DANDKHORA BLOCK
HASANGANJ BLOCK
MANSAHI BLOCK
PARANPUR BLOCK